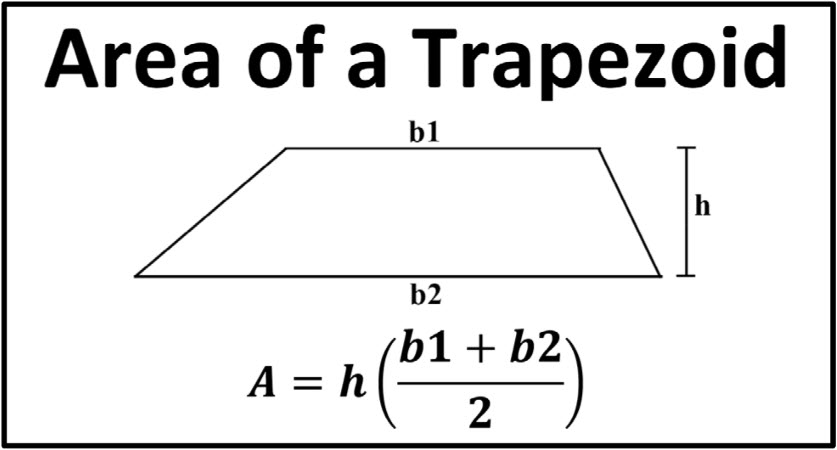
You can find the area of a trapezoid by using the formula
\(\displaystyle \text{Area} = h\cdot \frac{b_1+b_2}{2} \)
where \(b_1\) and \(b_2\) are the two parallel sides (or “bases”) and \(h\) is the height of the trapezoid.
Notes
Practice Problems
Find the area of the following trapezoids.
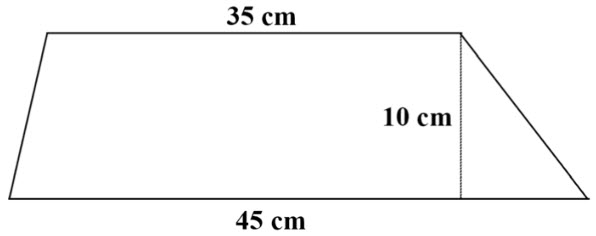
\(\textbf{1)}\)

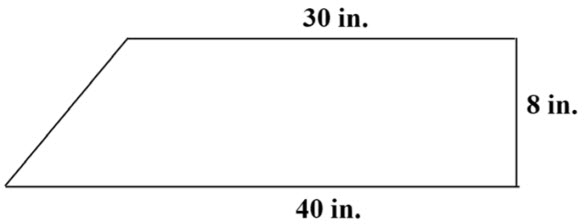
\(\textbf{2)}\)

\(\textbf{3)}\)
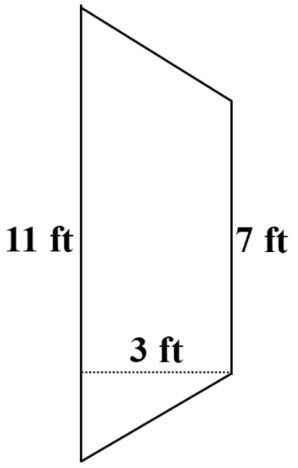

\(\textbf{4)}\) Find the area of the trapezoid with the following vertices. \((0,0), (2,8), (6,8), (8,0)\)
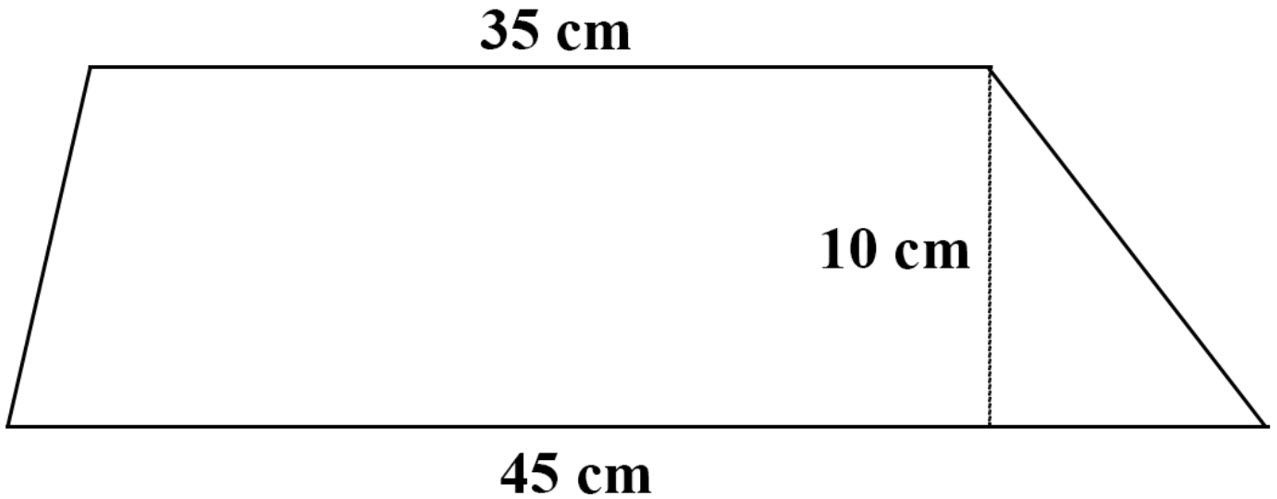
\(\textbf{5)}\) Find the area of the following trapezoid.
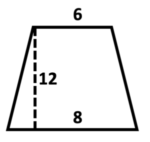
Challenge Problems
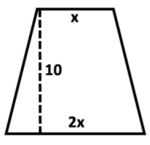
\(\textbf{6)}\) Solve for x if the area = \( 200 \) units\(^2 \).
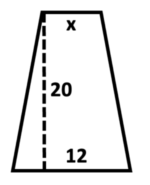
\(\textbf{7)}\) Solve for y if the area = \( 196 \) units\(^2 \).
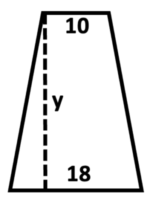
\(\textbf{8)}\) Solve for x if the area = \( 90 \) units\(^2 \).
See Related Pages\(\)
\(\bullet\text{ Geometry Homepage}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\text{All the Best Topics…}\)
\(\bullet\text{ Trapezoid Area Calculator (Omnicalculator.com)}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\) \(\)
\(\)
\(\bullet\text{ Area and Perimeter of Rectangles}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\)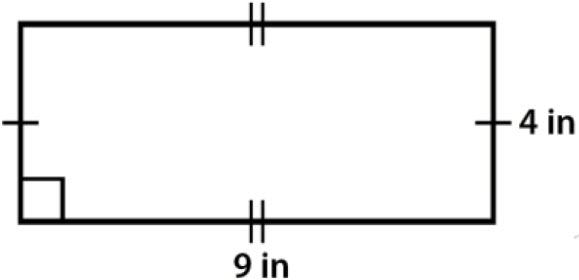 \(\,\, A=bh, \,\, P=2b+2h…\)
\(\,\, A=bh, \,\, P=2b+2h…\)
\(\bullet\text{ Area and Perimeter of Triangles}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\)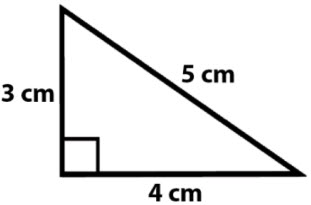 \(\,\, A=\frac{1}{2}bh, \,\, P=s_1+s_2+s_3…\)
\(\,\, A=\frac{1}{2}bh, \,\, P=s_1+s_2+s_3…\)
\(\bullet\text{ Area and Circumference of Circles}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\) \(\,\, A= \pi r^2, \,\,C=2 \pi r…\)
\(\,\, A= \pi r^2, \,\,C=2 \pi r…\)
\(\bullet\text{ Area of Trapezoids}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\) \(A=\frac{1}{2}(b_1+b_2)\cdot h…\)
\(A=\frac{1}{2}(b_1+b_2)\cdot h…\)
\(\bullet\text{ Area of Compound Figures}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\) \(\)
\(\)
\(\bullet\text{ Andymath Homepage}\)
In Summary
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral containing a pair of parallel sides, called the bases, and two non-parallel sides, called the legs. They are often referred to as a “trapezium” outside of the United States. The area of a trapezoid is typically covered in a high school geometry class. It is often introduced along with other two-dimensional shapes, such as triangles and circles, and students learn how to calculate the area of each using specific formulas. The formulas can also be used to find particular parts of the trapezoids given the area. Isosceles trapezoids are a special case where the legs and base angles are congruent.
About Andymath.com
Andymath.com is a free math website with the mission of helping students, teachers and tutors find helpful notes, useful sample problems with answers including step by step solutions, and other related materials to supplement classroom learning. If you have any requests for additional content, please contact Andy at tutoring@andymath.com. He will promptly add the content.
Topics cover Elementary Math, Middle School, Algebra, Geometry, Algebra 2/Pre-calculus/Trig, Calculus and Probability/Statistics. In the future, I hope to add Physics and Linear Algebra content.
Visit me on Youtube, Tiktok, Instagram and Facebook. Andymath content has a unique approach to presenting mathematics. The clear explanations, strong visuals mixed with dry humor regularly get millions of views. We are open to collaborations of all types, please contact Andy at tutoring@andymath.com for all enquiries. To offer financial support, visit my Patreon page. Let’s help students understand the math way of thinking!
Thank you for visiting. How exciting!