Andymath.com features free videos, notes, and practice problems with answers! Printable pages make math easy. Are you ready to be a mathmagician?
Lesson
Notes
Questions
For numbers 1-7, find the probabilities using the following 2 way table.
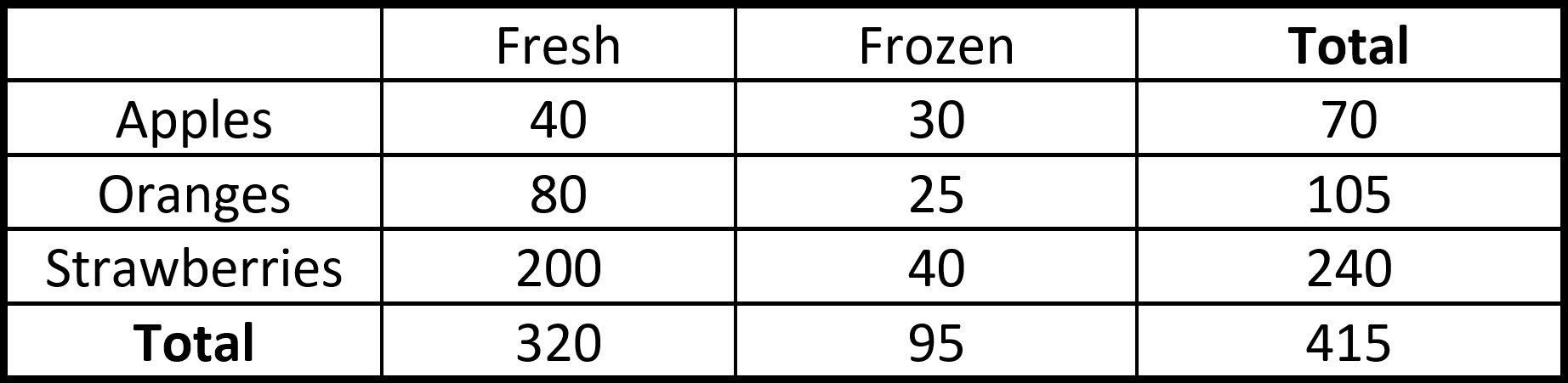
\(\textbf{1)}\) P (apples | fresh)
\(\textbf{2)}\) P (oranges given fresh)
\(\textbf{3)}\) P (fresh | apples)
\(\textbf{4)}\) P (apples | strawberries)
Same table as above

\(\textbf{5)}\) P (fresh | strawberries)
\(\textbf{6)}\) P (apples | frozen)
\(\textbf{7)}\) P (frozen given apples)
For numbers 8-9, find the probabilities using the following Venn Diagram.
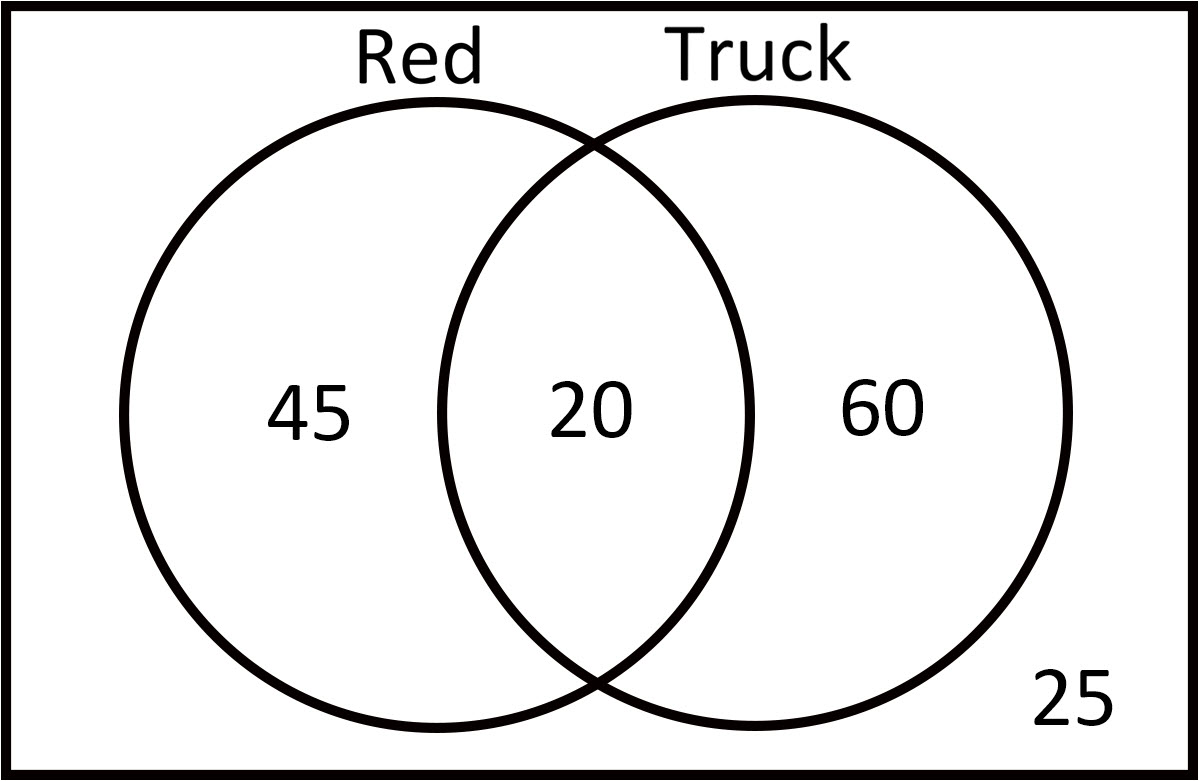
\(\textbf{8)}\) P (red | truck)
\(\textbf{9)}\) P (truck | red)
For numbers 10-11, find the probabilities if 2 dice are rolled and the sum is calculated. Use the below table to help you.
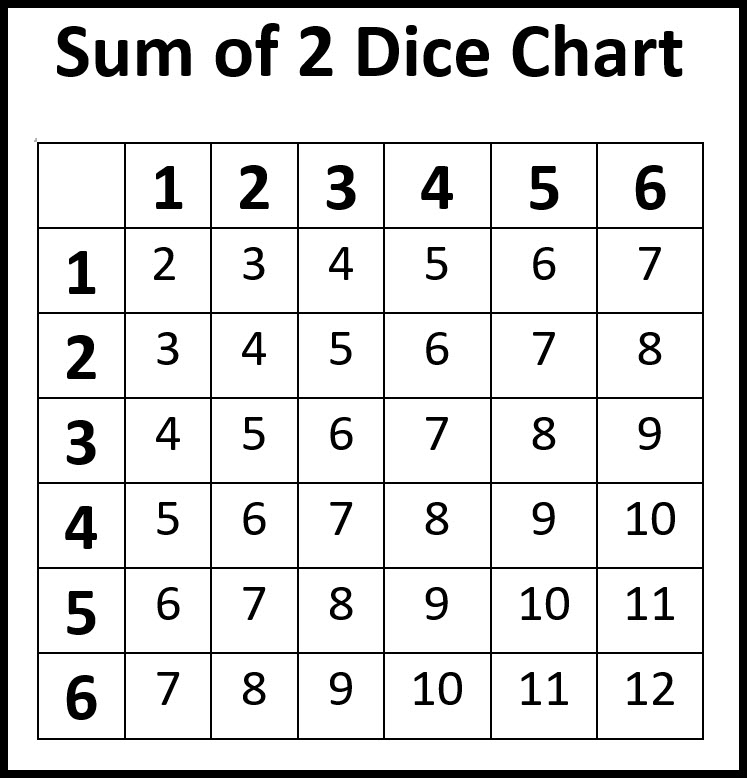
\(\textbf{10)}\) P (\(6|\)even)
\(\textbf{11)}\) P (even\(|6\))
See Related Pages\(\)
\(\bullet\text{ Statistics Homepage}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\text{All the Best Topics…}\)
\(\bullet\text{ Independent Events}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,P(A \cap B)=P(A)P(B)…\)
\(\bullet\text{ Mutually Exclusive Events}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,P(A \cap B)=0…\)
\(\bullet\text{ Venn Diagrams}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\) …
…
\(\bullet\text{ Tree Diagrams}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\) …
…
\(\bullet\text{ Two-Way Tables}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\) …
…
In Summary
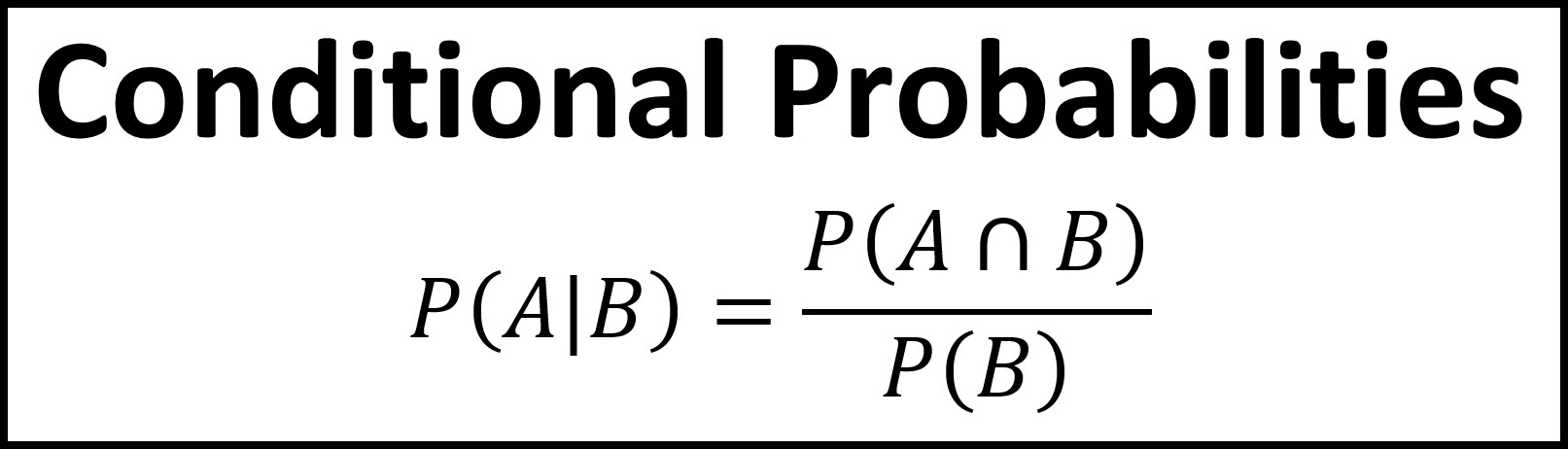
Conditional probability is a fundamental concept in probability theory that deals with the probability of an event occurring given that another event has already occurred. The formal definition of conditional probability is the probability of an event A occurring given that event B has already occurred, written as P(A|B). \(P(A \mid B) = \frac{P(A \cap B)}{P(B)}\)
Understanding and applying conditional probability is important for making informed decisions and predictions in various fields, including economics, medicine, and engineering. It can also be used to solve real-world problems, such as calculating the probability of a disease occurring based on certain risk factors.
Conditional probability is typically introduced in a probability and statistics course.
Real world examples of Conditional Probabilities
Medical diagnosis: A doctor may use conditional probability to determine the likelihood of a patient having a certain disease based on the presence of certain symptoms. For example, the probability of a patient having influenza may be higher if they have a fever and cough compared to if they only have a fever.
Weather forecasting: Meteorologists may use conditional probability to predict the likelihood of certain weather events occurring based on current conditions. For example, the probability of it raining may be higher if there is a low pressure system and clouds in the area compared to if there is clear blue sky.
Credit risk assessment: Financial institutions may use conditional probability to assess the risk of a borrower defaulting on a loan based on certain characteristics, such as their credit score and income. For example, the probability of a borrower defaulting on a loan may be higher if they have a low credit score and a low income compared to if they have a high credit score and a high income.
Traffic analysis: Transportation planners may use conditional probability to predict traffic patterns based on the time of day and day of the week. For example, the probability of heavy traffic on a highway during rush hour on a weekday may be higher compared to during the late night on a weekend.
Marketing: Marketers may use conditional probability to determine the likelihood of a customer making a purchase based on their past behavior and characteristics. For example, the probability of a customer making a purchase may be higher if they have made a purchase in the past and have a high income compared to if they have not made a purchase in the past and have a low income.
Math topics that use Conditional Probabilities
Bayesian statistics: Bayesian statistics is a branch of statistics that uses Bayes’ theorem to update probability estimates based on new data. Bayes’ theorem involves the use of conditional probabilities to calculate the probability of an event occurring based on prior knowledge.
Markov chains: A Markov chain is a mathematical system that undergoes transitions from one state to another according to certain probabilistic rules. Conditional probabilities are used to describe the probability of transitioning from one state to another in a Markov chain.
Decision trees: A decision tree is a graphical representation of a decision-making process in which an initial set of options is presented, and based on the chosen option, additional options are presented until a final decision is made. Conditional probabilities are used to represent the likelihood of certain outcomes occurring based on the choices made in the tree.
Machine learning: Machine learning algorithms often use conditional probabilities to make predictions or decisions based on data. For example, a machine learning model may use conditional probabilities to classify a given input into one of several categories based on the features of the input.
Queueing theory: Queueing theory is a branch of mathematics that deals with the modeling of waiting lines or queues. Conditional probabilities are used to describe the probability of certain events occurring in a queue, such as the probability of a customer being served within a certain time period.
About Andymath.com
Andymath.com is a free math website with the mission of helping students, teachers and tutors find helpful notes, useful sample problems with answers including step by step solutions, and other related materials to supplement classroom learning. If you have any requests for additional content, please contact Andy at tutoring@andymath.com. He will promptly add the content.
Topics cover Elementary Math, Middle School, Algebra, Geometry, Algebra 2/Pre-calculus/Trig, Calculus and Probability/Statistics. In the future, I hope to add Physics and Linear Algebra content.
Visit me on Youtube, Tiktok, Instagram and Facebook. Andymath content has a unique approach to presenting mathematics. The clear explanations, strong visuals mixed with dry humor regularly get millions of views. We are open to collaborations of all types, please contact Andy at tutoring@andymath.com for all enquiries. To offer financial support, visit my Patreon page. Let’s help students understand the math way of thinking!
Thank you for visiting. How exciting!

