Andymath.com features free videos, notes, and practice problems with answers! Printable pages make math easy. Are you ready to be a mathmagician?
Notes
See Related Pages\(\)
\(\bullet\text{ Statistics Homepage}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\text{All the Best Topics…}\)
\(\bullet\text{ Margin of Error}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\)
\(\bullet\text{ Confidence Intervals}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\)
\(\bullet\text{ Standard Error}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\)
\(\bullet\text{ Confidence Level}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\)
\(\bullet\text{ Type I and Type II Errors}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\)
\(\bullet\text{ One Sample z-test}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\)
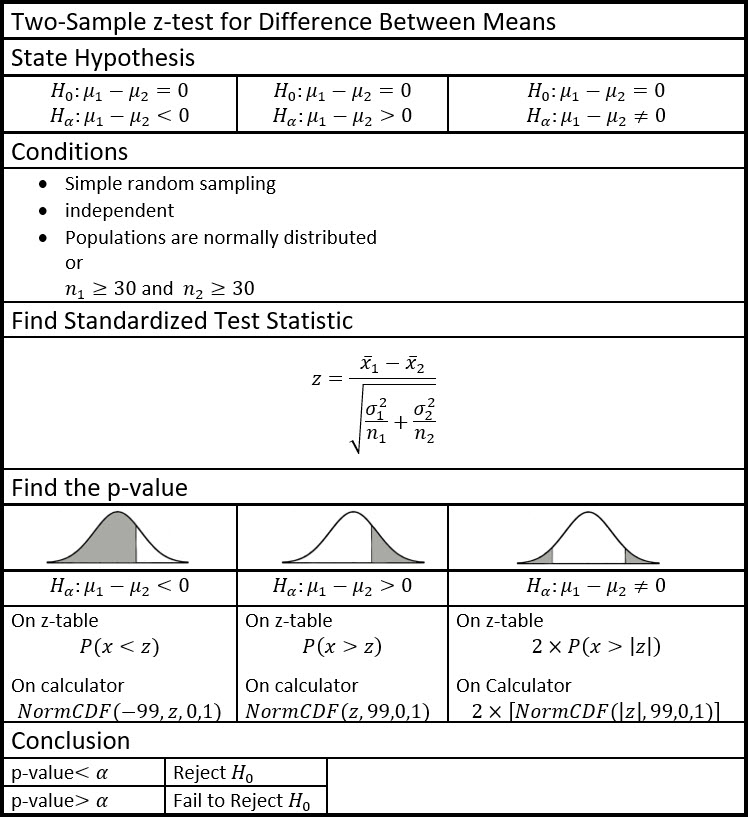
\(\bullet\text{ Two Sample z-test for Difference Between Means}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\)
\(\bullet\text{ Hypothesis Test- Difference Between Proportions}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\)
\(\bullet\text{ Chi-squared test}\)
\(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\)
In Summary
The Two Sample z-test is a statistical procedure used to determine whether there is a significant difference between the means of two independent groups. This test is often used in situations where researchers want to compare the mean of one group to the mean of another group, such as in A/B testing or medical trials.
It calculates the probability (p-value) that the difference between the means of two groups is due to random chance. If the p-value is below a certain level (usually 0.05), the difference between the means is considered statistically significant, and we can conclude that there is a significant difference between the means of the two groups.
Understanding the Two Sample z-test is important for researchers, data scientists, and statisticians because it allows them to make informed decisions about the results of their studies. By understanding the principles behind the Two Sample z-test, researchers can accurately interpret the results of their studies and make informed conclusions about their findings.
The Two Sample z-test for Difference Between Means is typically covered in a course on statistics or data analysis. This test is typically introduced in an intermediate or advanced level statistics course, and requires a basic understanding of probability, hypothesis testing, and statistical inference.
Common mistakes with Two Sample z-test for Difference Between Means: One common mistake when using the Two Sample z-test is failing to meet the assumptions of the test. These assumptions include independence of the samples, normality of the distributions, and equal variances. If these assumptions are not met, the results of the test may be invalid. Another mistake is failing to properly specify the null and alternative hypotheses, which can lead to incorrect conclusions about the data.
The Two Sample z-test for Difference Between Means was developed by statisticians in the early 20th century, and has been refined and improved upon over the years. It is based on the work of many pioneering statisticians, including Ronald Fisher, who is considered one of the founders of modern statistical theory.
Other statistical tests that are related to the Two Sample z-test include the One Sample z-test, the t-test for Difference Between Means, and the ANOVA (Analysis of Variance). These tests are all used to compare the means of different groups and are commonly used in research and data analysis.
Real world examples of Two Sample z-test for Difference Between Means
A pharmaceutical company wants to compare the effectiveness of two different drugs for reducing blood pressure. The company conducts a clinical trial in which some participants are given Drug A and others are given Drug B. The company can use a two-sample z-test to determine whether there is a significant difference in the average reduction in blood pressure between the two groups.
A marketing research firm wants to know whether there is a significant difference in the average amount of time that people spend on a website depending on whether they are shown a banner ad or a pop-up ad. The firm can use a two-sample z-test to compare the mean time spent on the website by people who saw the banner ad to the mean time spent by those who saw the pop-up ad.
A sports team wants to know whether there is a significant difference in the average number of points scored by its players during home games versus away games. The team can use a two-sample z-test to compare the mean number of points scored by the team at home to the mean number of points scored by the team on the road.
A school district wants to know whether there is a significant difference in the average test scores of students who receive after-school tutoring versus those who do not. The district can use a two-sample z-test to compare the mean test scores of students who receive tutoring to the mean test scores of those who do not.
A human resources department wants to determine whether there is a significant difference in the average salaries of men and women working at the same job level within the company. The department can use a two-sample z-test to compare the mean salary of men to the mean salary of women.
About Andymath.com
Andymath.com is a free math website with the mission of helping students, teachers and tutors find helpful notes, useful sample problems with answers including step by step solutions, and other related materials to supplement classroom learning. If you have any requests for additional content, please contact Andy at tutoring@andymath.com. He will promptly add the content.
Topics cover Elementary Math, Middle School, Algebra, Geometry, Algebra 2/Pre-calculus/Trig, Calculus and Probability/Statistics. In the future, I hope to add Physics and Linear Algebra content.
Visit me on Youtube, Tiktok, Instagram and Facebook. Andymath content has a unique approach to presenting mathematics. The clear explanations, strong visuals mixed with dry humor regularly get millions of views. We are open to collaborations of all types, please contact Andy at tutoring@andymath.com for all enquiries. To offer financial support, visit my Patreon page. Let’s help students understand the math way of thinking!
Thank you for visiting. How exciting!